Training
On
Oracle Hyperion Products Suite
&
Oracle Business Intelligence
Enterprise Edition
On
Oracle Hyperion Products Suite
&
Oracle Business Intelligence
Enterprise Edition
Hyperion Product Suite

What is Essbase?
It is a multidimensional database that enables Business Users to analyze Business data in multiple views/prospective and at different consolidation levels. It stores the data in a multi dimensional array.
Minute->Day->Week->Month->Qtr->Year
Product Line->Product Family->Product Cat->Product sub Cat
Product Line->Product Family->Product Cat->Product sub Cat
Typical Data Warehouse

Life Cycle Of Essbase
1.Creating the Database
2.Dimensional Building
3.Data Loading
4.Performing the Calculations
5.Generating the Reports
2.Dimensional Building
3.Data Loading
4.Performing the Calculations
5.Generating the Reports

HYPERION “Essbase” Components
1) Essbase Analytic Server (Essbase Server)
2) Essbase Administration Server (User Interface)
3) Essbase Integration Services (RDBMS:-Essbase)
4) Essbase Spread Sheet Services
5) Essbase Provider Services.
6) Essbase Smart-view
7) Essbase Studio (New Feature)
Architecture
2) Essbase Administration Server (User Interface)
3) Essbase Integration Services (RDBMS:-Essbase)
4) Essbase Spread Sheet Services
5) Essbase Provider Services.
6) Essbase Smart-view
7) Essbase Studio (New Feature)
Essbase Architecture
1.Client tier
2.Middle Tier (App tier)
3.Database tier
2.Middle Tier (App tier)
3.Database tier
Architecture

Contents
Overview (OLAP)
Multidimensional Analysis
Multidimensional Analysis
* Multidimensional Analysis Introduction
* Operations In multidimensional Analysis
* Multidimensional Data Model
* Multi-Dimensional vs. Relational
* Operations In multidimensional Analysis
* Multidimensional Data Model
* Multi-Dimensional vs. Relational
Overview of system 9.x/11.x
* Hyperion System 9 Smart view
* Hyperion System 9 BI+ Interactive reporting
* Hyperion System 9 BI+ Analytic services
* Hyperion system 9 shared services
* Hyperion system 9 White Board
* Hyperion System 9 BI+ Interactive reporting
* Hyperion System 9 BI+ Analytic services
* Hyperion system 9 shared services
* Hyperion system 9 White Board
Introduction to Essbase
Online Analysis Processing(OLAP)
It enables analysts, managers and executives to gain insight into data through fast, consistent, interactive access to a wide variety of possible views of information that has been transformed from raw data to reflect the real dimensionality of the enterprise as understood by the user.

Overview of OLAP
OLAP can be defined as a technology which allows the users to view the aggregate data across measurements (like Maturity Amount, Interest Rate etc.) along with a set of related parameters called dimensions (like Product, Organization, Customer, etc.)
Relational OLAP (ROLAP)
Relational and Specialized Relational DBMS to store and manage warehouse data
OLAP middleware to support missing pieces
• Optimize for each DBMS backend
• Aggregation Navigation Logic
• Additional tools and services
Example: Micro strategy, MetaCube (Informix)
OLAP middleware to support missing pieces
• Optimize for each DBMS backend
• Aggregation Navigation Logic
• Additional tools and services
Example: Micro strategy, MetaCube (Informix)
Multidimensional OLAP (MOLAP)
Domain-specific enrichment
- Array-based storage structures
- Direct access to array data structures
- Example: Essbase (Arbor), Accumate (Kenan)
Domain-specific enrichment

Key Features of OLAP applications
- Multidimensional views of data
- Calculation-intensive capabilities
- Time intelligence
**Key to OLAP systems are multidimensional databases.
- Multidimensional databases not only consolidate and calculate data; they also provide retrieval and calculation of a variety of data subsets.
- A multidimensional database supports multiple views of data sets for userswho need to analyze the relationships between data categories
Ex: Did this product sell better in particular regions? Are there regional trends?
Did customers return Product A last year? Were the returns due to product defects?
Did customers return Product A last year? Were the returns due to product defects?
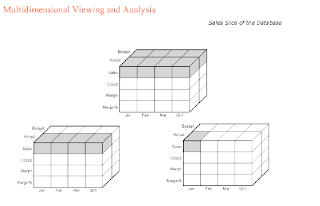
What is Multidimensional Analysis
Multidimensional Analysis
Multidimensional Analysis
A multidimensional database supports multiple views of data sets for users who need to analyze the relationships between data categories. For example, a marketing analyst might want answers to the following questions:
- How did Product A sell last month? How does this figure compare to sales in the same month over the last five years? How did the product sell by branch, region, and territory?
- Did this product sell better in particular regions? Are there regional trends?
Multidimensional databases consolidate and calculate data to provide different views. Only the database outline, the structure that defines all elements of the database, limits the number of views. With a multidimensional database, users can pivot the data to see information from a different viewpoint, drill down to find
more detailed information, or drill up to see an overview.


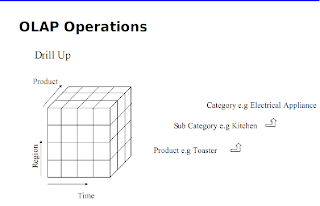


Operations In multidimensional Analysis
Aggregation (roll-up)
- dimension reduction: e.g., total sales by city
- summarization over aggregate hierarchy: e.g., total sales by city and year -> total sales by region and by year
Selection (slice) defines a sub cube
- e.g., sales where city = Palo Alto and date = 1/15/96
Navigation to detailed data (drill-down)
- e.g., (sales - expense) by city, top 3% of cities by average income
Visualization Operations (e.g., Pivot)
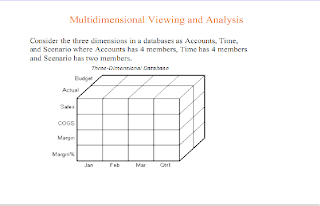
Multidimensional Data Model
Database is a set of facts (points) in a multidimensional space
A fact has a measure dimension
A fact has a measure dimension
- quantity that is analyzed, e.g., sale, budget, Operating Exp,
A set of dimensions on which data is analyzed
- e.g. , store, product, date associated with a sale amount
Dimensions form a sparsely populated coordinate system
Each dimension has a set of attributes
- e.g., owner city and county of store
Attributes of a dimension may be related by partial order
- Hierarchy: e.g., street > county >city
- Lattice: e.g., date> month>year, date>week>year










The use ofHR analyticsis no longer just the domain of those who are passionate about data and statistics. Everyone is now well aware that analytics can offer insights into an organization that can help them increase revenue and reduce costs. Yet, despite the fact that the goals of analytics are clear and simple, large swaths of the workforce remain unaware of what the field offers and how it is being deployed.
ReplyDelete